Strategy
| Platform | Strategy | Indicators | Delivery |
| Nanopore PromethION | 1D Library ≥100× Sequencing Depth | Single base error rate <0.01% | Database construction and sequencing: 10 working days Standard analysis: 6 working days Advanced analysis: According to the actual analysis content |
| PacBio Sequel | 10kb SMRTbell Library ≥100× Sequencing Depth | Single base error rate <0.01% | Database construction and sequencing: 16 working days Standard analysis: 6 working days Advanced analysis: According to the actual analysis content |
Note: For mitochondrial/chloroplast genome sequencing, a total DNA sample with a mitochondrial/chloroplast genome content of more than 10% is required.
Analysis
- Data output and quality control
- Complete assembly and evaluation of assembly results
- Genome annotation
- Genomic circle map
Results
Genome Structure Annotation
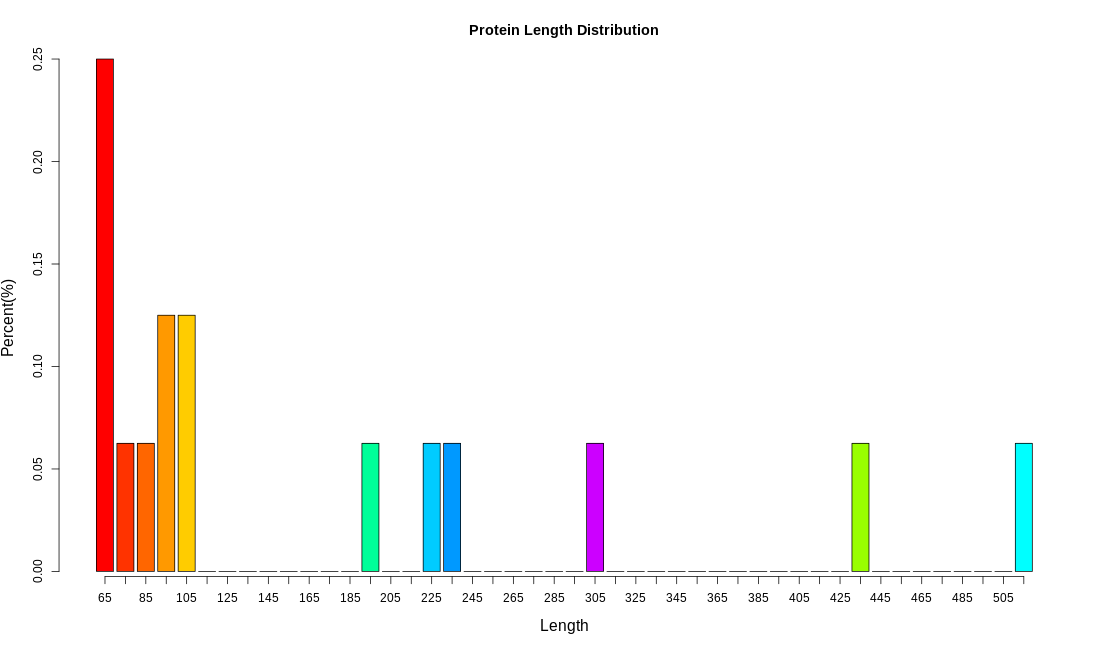
Exon Length Distribution
Genome Circle Map
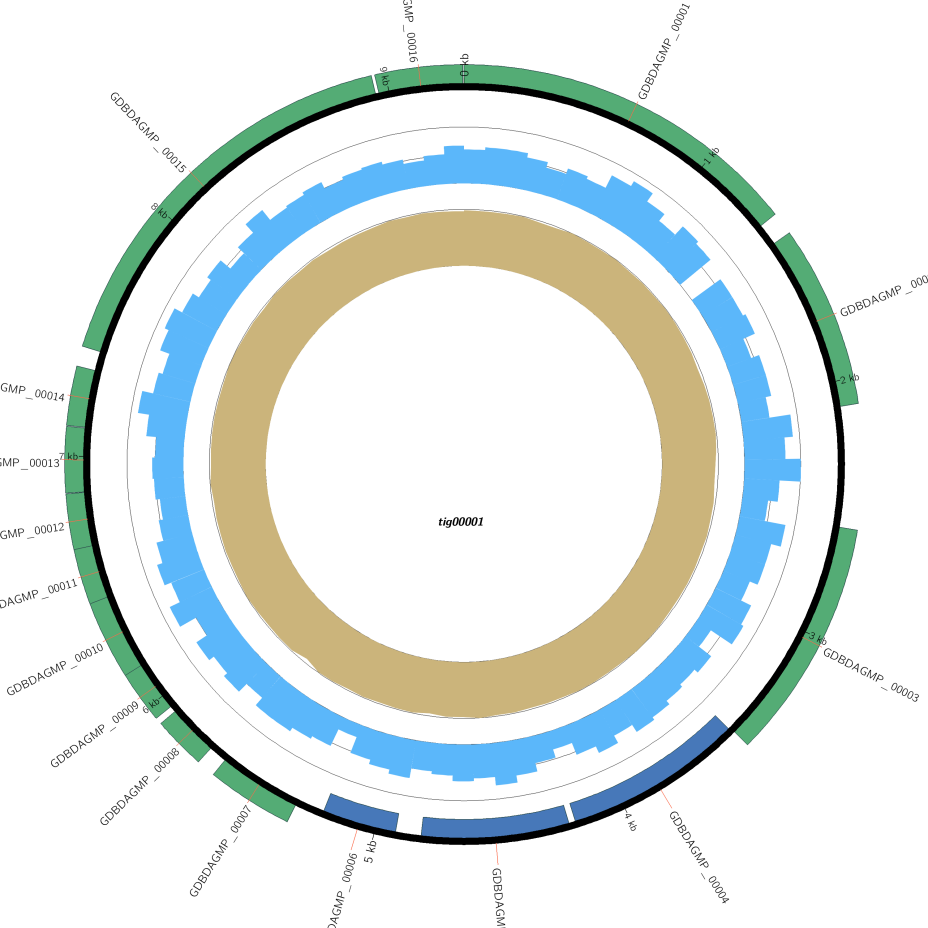
Depth distribution, GC content distribution, coding gene (sense strand), coding gene (negative sense strand) from inside to the outside respectively
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
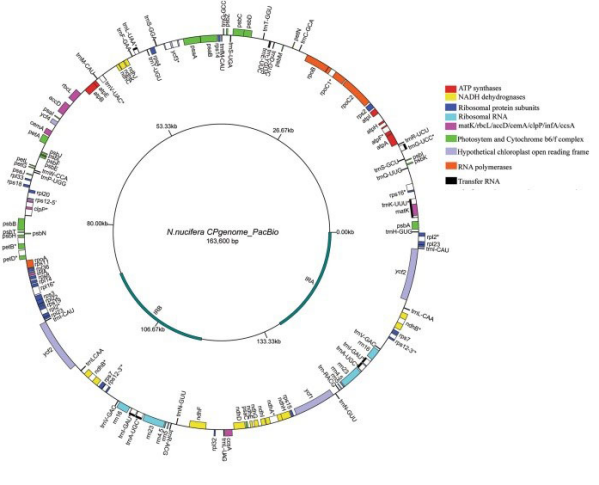
Construction of complete chloroplast genome map of lotus root based on Pacbio
Background
The lotus is an ancient dicotyledon left over from the late Cretaceous. The acquisition of chloroplast genome sequence information is of great significance for revealing the evolution of dicotyledons and the formation of plastids.
Methodology
Researchers from Wuhan University and Wuhan Futuromics used the PacBio RS II platform to obtain a high-quality lotus chloroplast genome map.A total of 105X PacBio data was produced to complete the map assembly, and 7X Sanger, 12X Sanger, and Illumina Miseq assembly results were used to evaluate the PacBio assembly results and assembly complexity.
Results
- Genome assembly results:
PacBio part: Assembled a complete circular genome sequence map of 163.6Kb, verified by PCR. Assembly completeness is 100%.
Illumina+PCR hole filling: Assembled 163.7Kb chloroplast genome with two gap regions. PCR verification found that a 152bp inverted repeat insert error, which may be caused by the short read length of the Illumina platform.
Sanger+PCR hole filling: Assembled 163.3Kb chloroplast genome. PCR verification found a 282bp deletion error in the ndhA region, which may be related to the low throughput of the Sanger sequencing platform.
- Genome feature analysis:
Start codons on the chloroplast genome of lotus and 8 other dicotyledonous plants were compared.
The lotus chloroplast genome contains a very complete set of chloroplast genes. Some chloroplast genes were lost during the evolution of angiosperms, such as the ndh gene related to photosynthesis; some genes were transferred from the chloroplast genome to the nuclear genome during the evolution process Medium, such as infA.
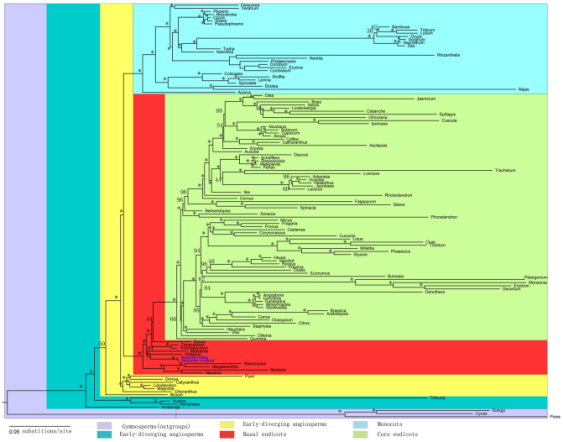
- System evolution analysis:
A phylogenetic tree was constructed by comparing the lotus with 79 chloroplast protein sequences of 56 other seed plants. The results showed that the lotus and a large land shrub genus Platanus vulgaris were sister branches. The lotus and saccharum also form a sister branch in the evolutionary tree, confirming the idea that the genus Nelumbo is an ancient dicotyledon; the genus Nelumbo differentiated about 170 million years ago, and the only two species of the genus, American lotus and Chinese lotus appeared 2 million years ago.
Chloroplast genome circle map of lotus root
Evolution analysis of lotus root
References: Wu. Z. H. et al. (2014) A precise chloroplast genome of Nelumbo nucifera (Nelumbonaceae) evaluated with Sanger, I llumina MiSeq, and PacBio RS I I sequencing platforms: insight into the plastid evolution of basal eudicots. BMC Plant Biology.