Product Advantages
Ultra-long read length, directly obtained transcript.
The average length of Iso-Seq is 10-12kb, much larger than the length of typical genes in general transcripts. It can easily span the complete transcript from the 5’end to the 3′-Poly A tail without splicing and directly measure the full length of the transcript. .
Accurately identify alternative splicing and reconstruct transcripts.
In the past, transcriptome research strategies were primarily based on second-generation short-read sequencing, using read assemblies to speculate the structure of the transcript. However, faced with the complexity of alternative splicing, incorrect predictions are commonplace. Using Iso-Seq, the full-length transcriptome can be accurately reconstructed and the transcript structure deduced.
Fusion gene identification and variable polyadenylation (APA) analysis.
Strategy
| RNA Sample | Library Construction | Sequencing Strategy |
| Sample ≥ 1μg, Concentration ≥300ng/μL | Reverse transcription to obtain the full-length cDNA, construct a 0.5-6Kb cDNA SMRTbell library | Suggested Data Size≥20Gb |
Analysis
| Reference Available | No Reference Available |
|
|
Results
Full-length transcript identification
Theoretically, the complete inserted reads have a 5’ primer on one end, a 3’ primer on the other end, and a polyA sequence just before the 3’ primer. Therefore, by judging the existence and positional relationship of the 5’primer, 3’primer, and polyA, we can classify the insert sequence. The insertion containing a 5’primer, 3’primer, and polyA with a correct relative position is considered a complete insert sequence, or a full-length read.
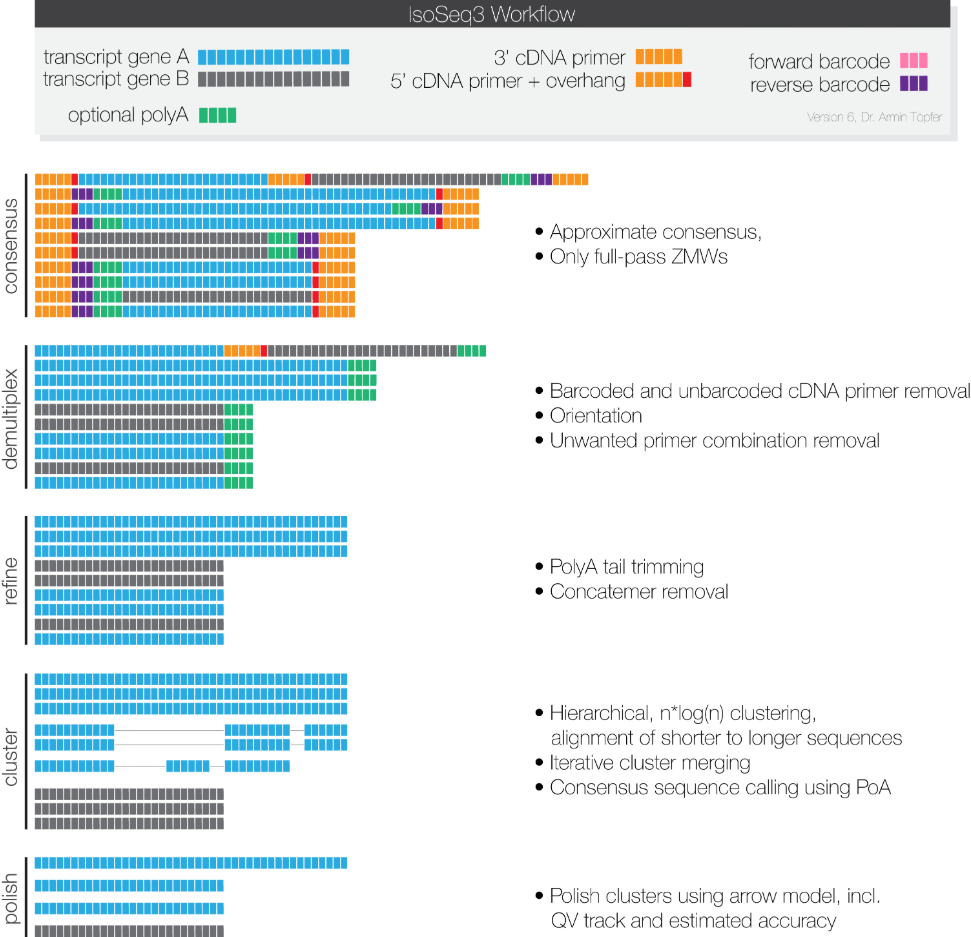
Full-length transcript identification process
Fusion gene identification
Fusion genes are chimeric genes formed by fusion of all or part of the sequences of two genes. It may be formed by chromosomal translocation, deletion in the middle, or chromosome inversion.
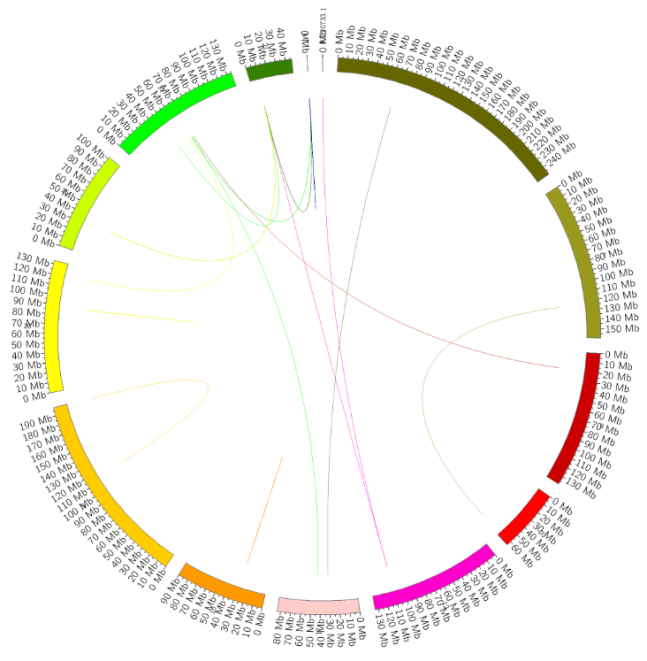
Fusion Gene Diagram
Comparison to Reference Gene Annotation
Compare the non-redundant transcript with the annotated reference transcript, extract the comparison result information, and merge the TGS annotation results with the reference annotation results.
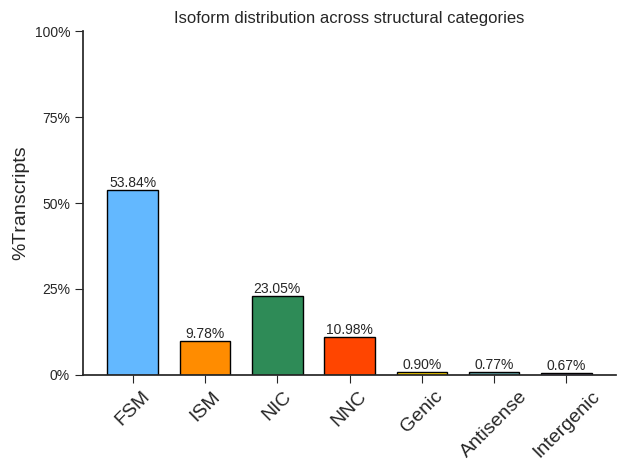
Distribution of different transcription isoforms
Alternative splicing analysis
The mRNA precursor produced by most eukaryotic gene transcription is spliced in one way to produce a mature mRNA molecule, so it is only translated into one particular protein. However, mRNA precursors of some genes produce different mRNA splicing isoforms through different splicing methods (selecting different splicing sites). This process is called alternative splicing, which is an important mechanism for regulating gene expression and generating proteome diversity.
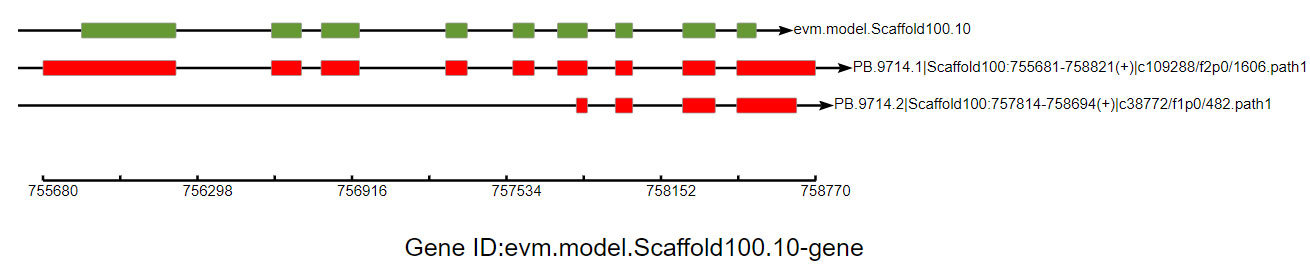
Alternative splicing event gene structure
Variable polyadenylation analysis (APA)
Alternative Polyadenylation (APA) is a gene regulation mechanism that is ubiquitous in eukaryotes. It means that a transcript can have different polyadenylation sites, so that different transcripts can have different coding sequences or different lengths of 3’untranslated regions (3’UTR). This allows a gene to produce multiple mRNA transcripts, affecting the function, stability, positioning and translation efficiency of mRNA.
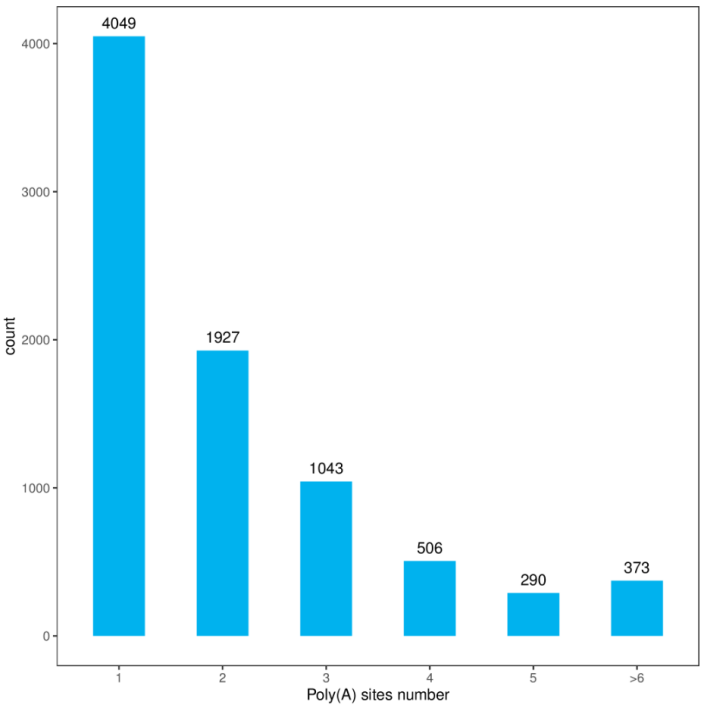
APA Site Count
Common Questions
1.What is the advantage of Iso-seq?
No need to interrupt splicing, no need for assembly. One can directly obtain the full-length transcript containing the 5’region, 3’UTR, and poly A tail, and accurately analyze species genome information such as variable splicing, gene fusion, and APA.
2.Do you need to construct a mixed library of different fragment sizes?
The hybrid library construction is for the previous RSII platform. After the upgrade of the Sequel platform, the fragment preference has been greatly improved. Generally speaking, the construction of a 0.5-6kb library can obtain results consistent with the real transcript distribution, so there is no need to construct a mixed library of different fragment sizes.
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
Case Analysis
PacBio long-read sequencing reveals the complexity of the corn transcriptome
Research Background
Maize (Zea mays) is an important crop in the world and a genetic model for studying the metabolic pathways of plant transcriptomes. The maize genome sequence was published in 2009, and its gene annotations were subsequently supplemented with EST and RNA-Seq transcriptome data. However, in RNA-Seq, short read lengths cannot provide the full-length sequence of the transcript, which limits the definition of alternative splicing forms. At the same time, short read length splicing will result in low-quality transcripts, leading to incorrect gene annotations.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory and other institutions used PacBio long-read sequencing technology to perform full-length transcriptome sequencing analysis on six maize tissues. This provided new insight on the transcriptome of existing maize B73 RefGen_v3, revealing the complexity of maize gene expression. Research results were subsequently published in Nature sub-journals.
Methodology
- Take 6 tissues (root, pollen, germ, endosperm, young ears, young tassels) from different developmental stages of maize inbred line B73, extract mRNA, mix evenly according to the equimolar ratio of cDNA, and construct 6 kinds of insert libraries (<1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–5, 4–6 and >5 kb). Add sequence specific barcodes to the different libraries, and run 46 SMRT Cells for full-length transcriptome sequencing.
- Perform second-generation RNA-Seq sequencing on 6 tissues, with three replicates for each sample.
- According to published methylation data, perform methylation analysis on isoform, IncRNA and non-IncRNA.
Research Results
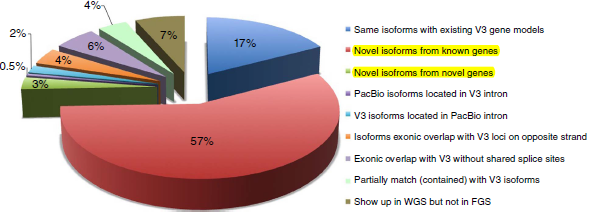
- 3,716,604 reads were obtained, and nearly half of the full-length transcript sequence (1,553,692, 42%) was filtered. After processing, 643,330 high-quality transcript sequences were obtained, of which 606,145 sequences (2%) could be aligned to the maize RefGen_v3 reference genome. After clustering, 111,151 isoforms were obtained, corresponding to 26943 genes, covering 70% of maize RefGen_v3 gene annotations. Among them, 57% of isoforms came from new isoforms at known gene loci; 2,803 (3%) new isoforms came from 2,253 new loci.
- There are 1704 highly reliable LncRNAs (average length of 463bp) in existing studies. This analysis yielded 878 LncRNAs, of which 11 were determined by existing studies, and the other 867 were newly discovered LncRNAs (with an average read length of 1kb).
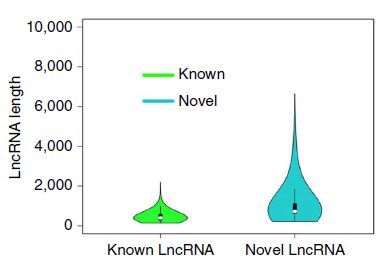
Known and Novel LncRNA length comparison
- The isoform analysis results of PacBio isoforms and Illumina short-read assembly were compared. Two analysis methods (Cufflinks and Trinity) were used to assemble the isoform for short-read data. The isoforms of PacBio were identified as only 22 % and 8%.This shows that the short-read transcriptome analysis method still has limitations in detecting isoforms, while PacBio long-reads can obtain accurate isoforms, especially complex situations where one gene corresponds to several isoforms.
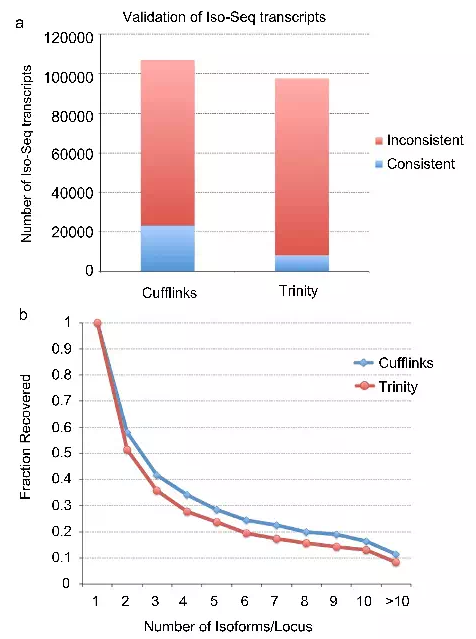
PacBio isoform compared to isoform constructed by short-read assembly
References
Bo Wang et al., (2016). Unveiling the complexity of the maize transcriptome by single-molecule long-read sequencing. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS.



